Tubes and pipes differences
You have probably heard the terms pipe and tube used interchangeably, and there's a good chance you aren't exactly sure what the difference is between them. Most people, even experts working in related industries, don't actually know. Pipes and Tubes may look similar because they are both of similar shape, with a hollow vacuum running through the center of them. But, you would be surprised that there are many differences between them.
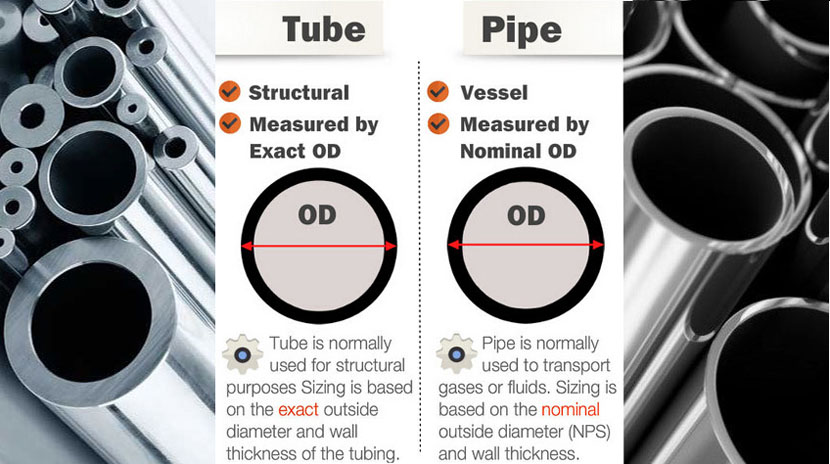
- Diameter and Thickness
Pipe and Tube diameters differ in how they are measured. The diameter of a pipe is referred to its nominal internal diameter and not the actual outside diameter. In contrast, the diameter of tube is measured by the actual outside diameter of the tube.
An important factor is how the wall thickness of the pipe and tube is measured. Pipe wall thickness is denoted by schedules; there are multiple schedules for each diameter. The larger the schedule number, the thicker the wall. The outside diameter remains constant over the entire schedule range.
Tubing wall thickness is measured by gauge number for thinner tubes and by fractions for thicker walled tubes.
- Tolerances
The tolerances of pipe and tube differ as well. Pipe has a looser tolerance than tube, which are commonly tighter in tolerances. Tolerance refers to diameter tolerance, wall thickness tolerance, straightness tolerance, and roundness tolerance.
- Manufacturing difference
The fabrication of pipe is easier than tube; most pipes are made from a flat strip of steel that is formed into a round shape and welded together. There is also seamless pipe that is not welded. This particular pipe is made from a solid round and more expensive; these are typically heavier wall pipe.
Tubing requires many more production operations to make a finished product. It is normally of a lot higher quality than pipe, resulting in increased testing and inspections. Pipe production far outweighs tubing production.
- Connection
Pipes are typically connected by threading the ends and screwing together with couplings, T’s, or elbows. Another common way of connecting pipes is welding them together or to other components, such as flanges.
Tubes can be connected by flaring, brazing, tube couplings, or welding. Pressures within the tube normally dictate the type of coupling used.
- Uses of pipes and tubes
Pipe is used for the transport of liquids and gases such as water, oil, natural gas, or propane. Pipe sizes and schedules are specified for the application depending on the internal pressure required of the material being transported, the volume of flow required and the material it is made of (if corrosion is an issue).
Tube, on the other hand, is used for many applications including structural, high pressure hydraulic systems, medical & food systems, boilers & heat exchangers, as well as several others. Tubing is made in many more grades of material and sizes than pipe; it can also be square or rectangular in shape, in addition to round.
- Cost and price
Due to the ease of manufacturing pipe, it is far less expensive and is manufactured in vast amounts, which also reduces the cost. Tubing, as mentioned above, is of a higher quality requiring more steps in the manufacturing process and thus is comparatively more expensive.
- Material
Piping is usually made of carbon steel or low alloy steel, while tubing is often made of mild steel, aluminum, brass, copper, chrome or stainless steel etc. Different material also lead to different cost and price.
- Mechanical and properties and chemical properties
For pipes the pressure rating, yield strength, ductibility properties are more important. However, for tubes. The hardness, tensile strength, high precision is the key to high quality. Those elements like C, Mn, S, P, Si are the main chemical elements for pipes, and there is few micro-elements requirements. While for tubing, the micro-elements are very important to the quality and process.
Pipes to delivered are in bundle or just bulk delivery. Because we just need to protect the pipes surface from serious damage and no need to protect from any light chafing. While tubes are usually wrapped with wooded box or thin film for each tube, especially for medical area tube.
- Surface finish
For outdoor field transporting or underground transporting, pipes need to be painted or coating to anti corrosion or oxidation. Tubes are sour cleaning or special polish treatment for particular field use.
- Quantity
For long transport or distributing, piping is often used in mass quantity and for long distance application. So, the order of pipes are usually large. While tubes may be used in small quantity.
- Pipe End and Tube End
Pipe ends are usually in plain or beveled so as to welding. while tubes are with coupling ends or specially end finish, like irregular ends, special screw thread etc.
Conclusion
It’s easy to see why the two are thought to be interchangeable, but everything from the way they measured to their actual use differs dramatically. Before beginning a project, make sure you know what you need and that you get the right type of pipe or tube.





